Có phải bạn đang muốn tìm bài viết về chủ đề “khan academy gibbs free energy” phải không? Chúng tôi cung cấp toàn bộ thông tin về chủ đề này tại website https://alophoto.net trong chuyển mục: 40+ blog chứng khoán mới nhất. Bạn sẽ tìm thấy câu trả lời chi tiết cho chủ đề này ngay bên dưới, vui lòng đọc tiếp đến cuối cùng để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề bạn đang tìm.
Để tải hình ảnh về điện thoại bạn có thể nhấn đè vào hình ảnh 2s sau đó chọn tải “Tải hình ảnh xuống” để tải ảnh về.
Để tải hình ảnh về máy tính bạn có thể nhấn chuột phải vào hình ảnh sau đó chọn “Lưu ảnh thành” để tải về
Top 56 hình ảnh liên quan đến chủ đề khan academy gibbs free energy
Có 26 hình ảnh liên quan đến chủ đề khan academy gibbs free energy, mời bạn xem ngay bên dưới:
Gibbs free energy and spontaneous reactions (video) | Khan Academy
Gibbs free energy and spontaneous reactions.
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 30696
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 13 hours ago
- Số lượt tải: 25792
- Likes: 9013
- Dislikes: 6

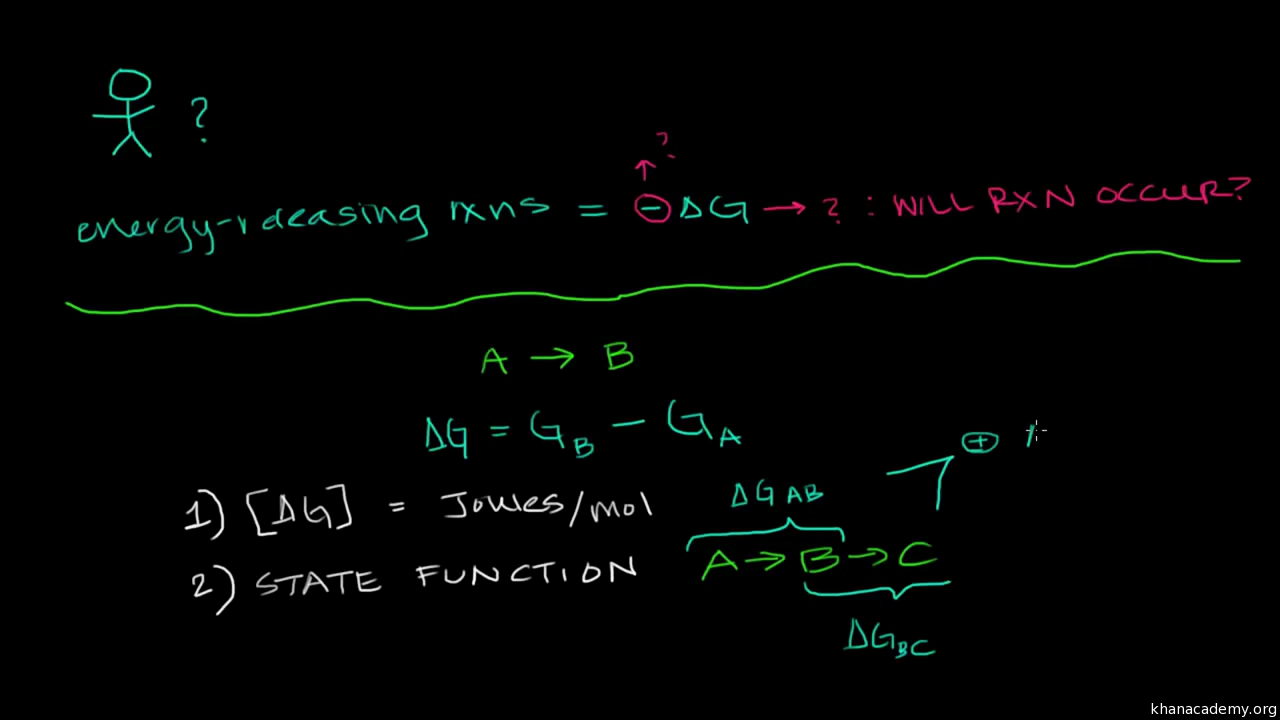
use change in Gibbs Free Energy to predict whether a reaction is going to spontaneously happen, whether it’s going to be spontaneous. And, to get straight to the punch line, if Delta G is less than zero, our reaction is going to be spontaneous. It’s going to be spontaneous. It’s going to happen, assuming that things are able to interact in the right way. It’s going to be spontaneous. Now, let’s think a little bit
Gibbs free energy and spontaneity (article) | Khan Academy
How the second law of thermodynamics helps us determine whether a process will be spontaneous, and using changes in Gibbs free energy to predict whether a reaction will be spontaneous in the forward or reverse direction (or whether it is at equilibrium!).
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 45862
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 13 hours ago
- Số lượt tải: 105913
- Likes: 1057
- Dislikes: 2
How the second law of thermodynamics helps us determine whether a process will be spontaneous, and using changes in Gibbs free energy to predict whether a reaction will be spontaneous in the forward or reverse direction (or whether it is at equilibrium!).
Gibbs free energy introduction (video) | Khan Academy
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 35507
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 40 minute ago
- Số lượt tải: 104997
- Likes: 9507
- Dislikes: 2

If you’re seeing this message, it means we’re having trouble loading external resources on our website.
More rigorous Gibbs free energy / spontaneity relationship (video) | Khan Academy
More formal understanding of why a negative change in Gibbs Free Energy implies a spontaneous, irreversible reaction.
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 104478
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 22 hours ago
- Số lượt tải: 107789
- Likes: 1206
- Dislikes: 9

comparing a irreversible to a reversible system. And this is true for all irreversible, spontaneous processes. And then if we assume that we’re
Introduction to Gibbs free energy (video) | Khan Academy
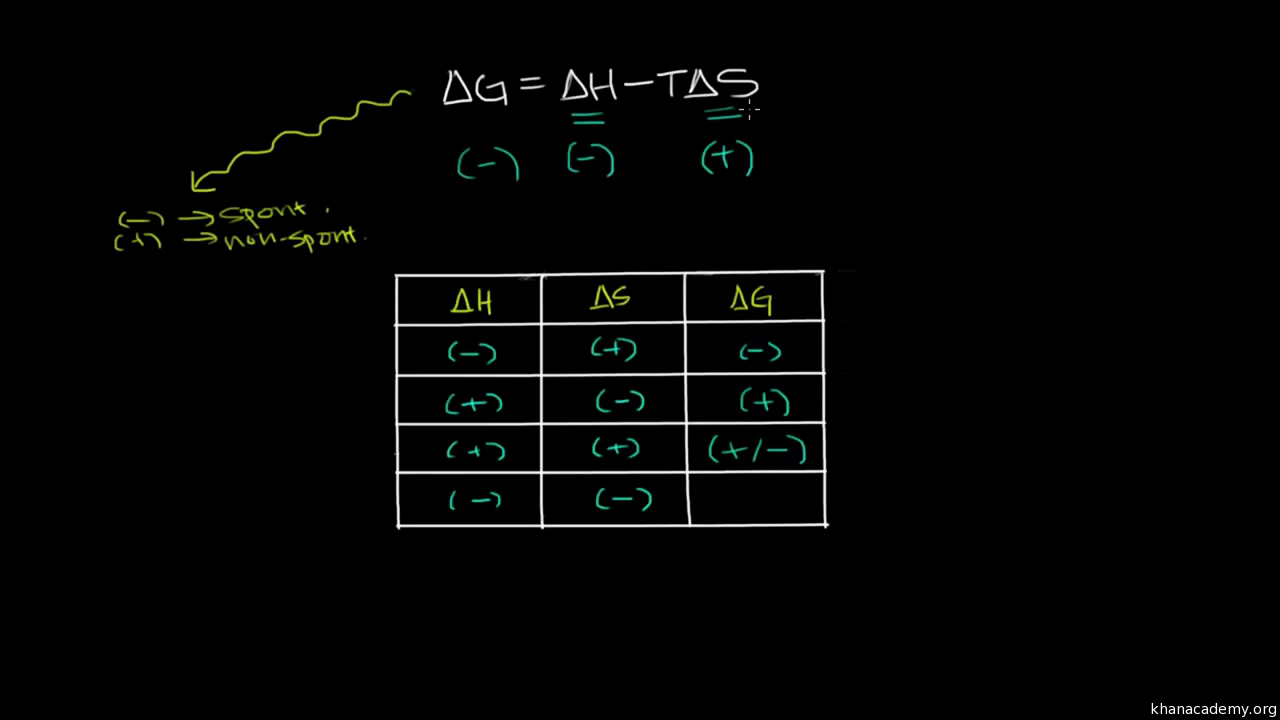
The standard Gibbs free energy change, ΔG°, indicates the thermodynamic favorability of a physical or chemical process. When ΔG° < 0, the process is thermodynamically favored. For a given process, the value of ΔG° can be calculated directly from the values of ΔH° and ΔS° using the following equation: ΔG° = ΔH° – TΔS°.
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 26129
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 38 minute ago
- Số lượt tải: 75685
- Likes: 6337
- Dislikes: 1

in enthalpy, delta H, minus the temperature in Kelvin, times the change in entropy, delta S. When delta G is less than zero, a chemical or physical process is favored in the forward direction. Therefore, we say that the forward process is thermodynamically favored. As an example, if we look at a reaction where reactants turn into products, if delta G is less than zero, the forward reaction as
Gibbs free energy introduction (video) | Khan Academy
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 88547
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 12 minute ago
- Số lượt tải: 83500
- Likes: 4869
- Dislikes: 7
If you’re seeing this message, it means we’re having trouble loading external resources on our website.
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 53231
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 52 minute ago
- Số lượt tải: 29450
- Likes: 6463
- Dislikes: 5
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 7026
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 12 hours ago
- Số lượt tải: 26213
- Likes: 4245
- Dislikes: 7

- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 60509
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 21 minute ago
- Số lượt tải: 76837
- Likes: 8966
- Dislikes: 1

Worked example: Determining the effect of temperature on thermodynamic favorability (video) | Khan Academy
When ΔH° and ΔS° for a reaction have the same sign, the thermodynamic favorability of the reaction depends on temperature. In this video, we’ll determine the thermodynamic favorability of a reaction with ΔH° < 0 and ΔS° < 0 at two different temperatures. We’ll also calculate the temperature at which the reaction changes from being thermodynamically favored to thermodynamically unfavored.
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 106748
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 16 hours ago
- Số lượt tải: 66611
- Likes: 7249
- Dislikes: 5

thermodynamically unfavorable. Since the change in enthalpy is negative, and the change in entropy is negative, whether or not delta G naught is negative depends on the temperature. To calculate the value for delta G naught, we’re going to use the following equation. Delta G naught is equal to delta H naught minus T delta S naught, where T is the temperature in kelvin. Next, we need to plug
Thermodynamic favorability and temperature (video) | Khan Academy
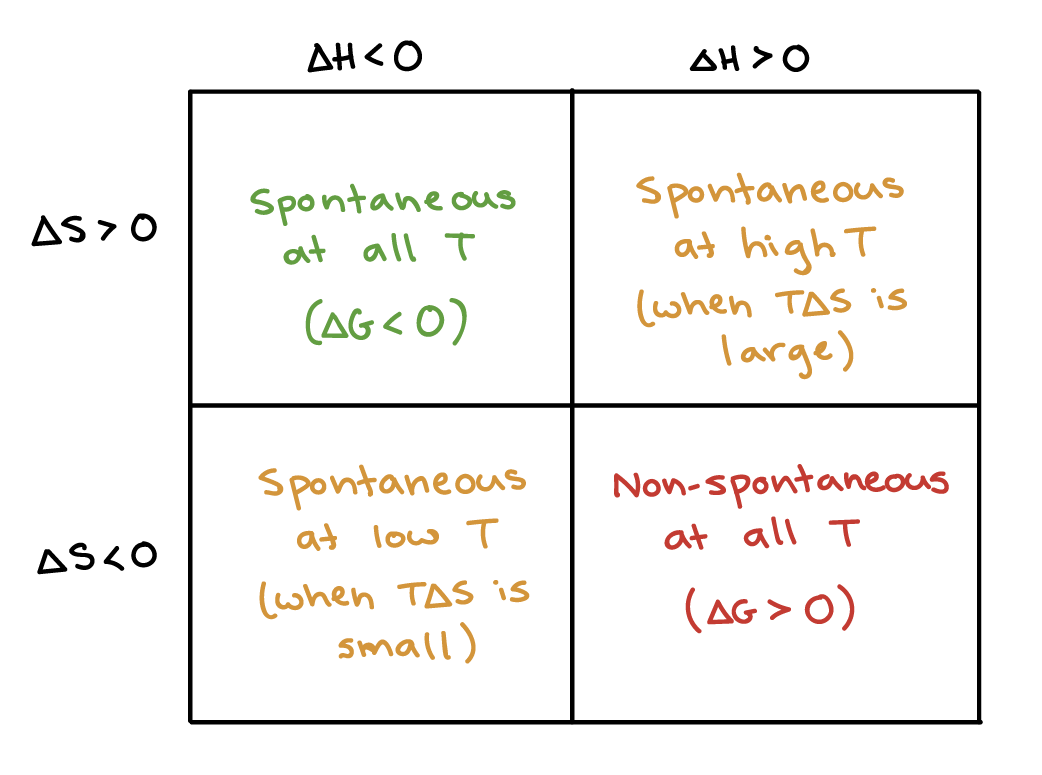
The temperature conditions under which a process is thermodynamically favored (ΔG° < 0) can be predicted from the signs of ΔH° and ΔS°. When ΔH° < 0 and ΔS° > 0, the process is favored at all temperatures. When ΔH° > 0 and ΔS° < 0, the process is favored at no temperature. When ΔH° < 0 and ΔS° < 0, the process is favored only at low temperatures. When ΔH° > 0 and ΔS° > 0, the process is favored only at high temperatures.
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 38390
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 5 hours ago
- Số lượt tải: 50951
- Likes: 9922
- Dislikes: 8

of ozone gas into oxygen gas. Since energy is released, this is an exothermic reaction, and delta H naught is negative. And since we’re going from 2 moles of gas on the reactant side to 3 moles of gas on the product side, that’s an increase in entropy. So delta S naught is positive. Since delta H naught is negative and delta S naught is positive, delta G naught for this reaction is less than zero at all temperatures. That means the forward reaction is thermodynamically favorable, and ozone gas would turn into oxygen gas, and this reaction would
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 13064
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 49 minute ago
- Số lượt tải: 9550
- Likes: 3174
- Dislikes: 1

Thermodynamics | Chemistry library | Science | Khan Academy
This unit is part of the Chemistry library. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic.
- Nguồn hình ảnh: www.khanacademy.org
- Số lượt xem hình ảnh: 85936
- Thời gian đăng ảnh: 32 minute ago
- Số lượt tải: 108715
- Likes: 5467
- Dislikes: 7
If you’re seeing this message, it means we’re having trouble loading external resources on our website.
Video for khan academy gibbs free energy Gibbs free energy and spontaneity | Chemistry | Khan Academy
- Source: Youtube
- Views: 24144
- Date: 49 minute ago
- Download: 2732
- Likes: 110
- Dislikes: 9
Thông tin liên quan về chủ đề khan academy gibbs free energy
Bạn có thể xem thêm một số thông tin mới nhất về chủ đề khan academy gibbs free energy trên Bing.
Gibbs free energy
Gibbs free energy equation
The standard gibbs free energy
Helmholtz free energy
Standard free energy change
Gibbs energy and spontaneity
Endergonic reaction
The standard Gibbs free energy of formation of is zero
Bạn vừa xem xong bài viết về chủ đề khan academy gibbs free energy. Nếu bạn thấy bài viết này hữu ích thì làm ơn hãy chia sẽ nó. Cảm ơn bạn rất nhiều.